Ovarian Cancer Risks in Indian Women: A Growing Concern
May 8, 2025
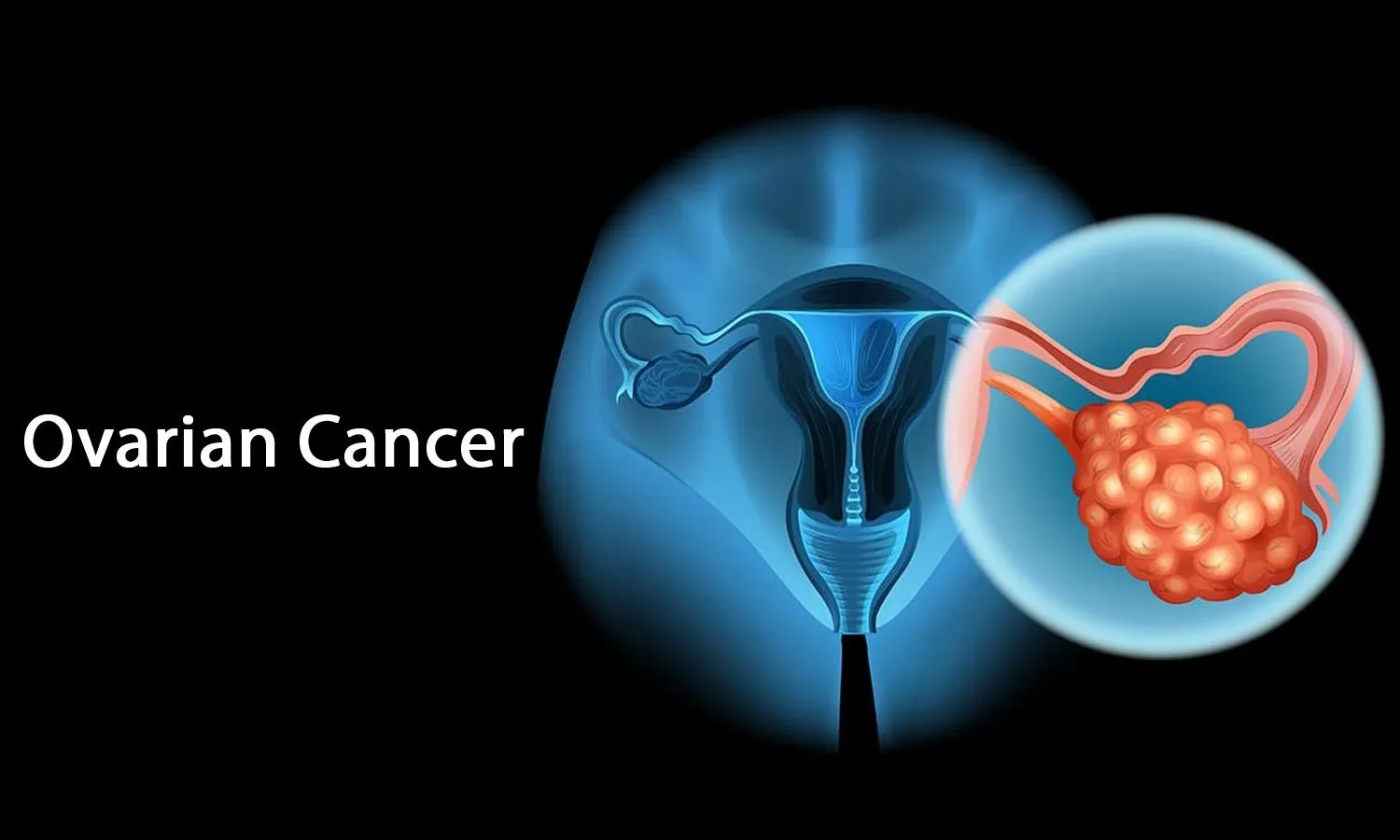
Ovarian cancer is a significant health challenge for women worldwide, and in India, it ranks as the third most common gynecological cancer. Understanding the risks and statistics associated with this disease is crucial for early detection, prevention, and improved outcomes for Indian women.
Incidence and Mortality in India
In 2022, India recorded a staggering 47,333 new cases of ovarian cancer, making it the second highest globally in terms of absolute numbers, only behind China. Sadly, the same year also saw 32,978 deaths due to this disease in India, the highest number worldwide. The age-adjusted incidence rate in India is estimated to be around 6.6 to 6.8 per 100,000 women. These figures highlight the urgent need for increased awareness, better screening methods, and improved access to treatment.
Key Risk Factors for Indian Women
Several factors can increase an Indian woman's risk of developing ovarian cancer:
Age: The risk significantly increases with age, with most cases diagnosed after menopause, particularly in women over 50.
Family History: A family history of ovarian, breast, or colorectal cancer, especially in first-degree relatives (mother, sister, daughter), elevates the risk. Inherited gene mutations, particularly in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, are significant risk factors.
Reproductive History:
Nulliparity: Women who have never been pregnant or carried a pregnancy to full term have a higher risk.
Late First Pregnancy: Having the first full-term pregnancy after age 35 is associated with increased risk.
Early Menarche and Late Menopause: Starting menstruation early or experiencing late menopause may also increase the risk.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese (BMI of 30 or higher) is linked to a higher risk of ovarian cancer.
Hormonal Factors:
Hormone Therapy After Menopause: Long-term use of estrogen-only or combined hormone replacement therapy has been associated with an increased risk.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and Endometriosis: These conditions may also slightly increase the risk.
Lifestyle Factors: While research is ongoing, factors like inactive lifestyles and improper eating habits may play a role. Some studies suggest a possible link between a high cholesterol intake and increased risk.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): Some studies indicate a potential association between in vitro fertilization (IVF) and a slightly increased risk of ovarian cancer.
Challenges in Early Detection
Ovarian cancer is often called a "silent killer" because early-stage symptoms are typically non-specific and can be easily mistaken for common ailments. These symptoms may include:
1. Bloating and abdominal discomfort
2. Pelvic pain or pressure
3. Feeling full quickly
4. Frequent urination
5. Changes in bowel habits
Unfortunately, by the time noticeable symptoms appear, the cancer has often advanced to later stages, making treatment more challenging and reducing the chances of survival.
The Need for Improved Strategies
Given the significant burden of ovarian cancer in India, several steps are crucial:
Increased Awareness: Educating women about the risk factors and potential symptoms is vital for early detection.
Strengthening Screening Programs: Currently, there is no widely recommended routine screening test for ovarian cancer in the general population. Research into effective screening methods suitable for the Indian context is essential.
Improved Access to Genetic Testing and Counseling: Making genetic testing for BRCA and other relevant gene mutations more accessible can help identify women at higher risk who may benefit from preventive measures.
Enhanced Diagnostic Methods: Investing in and utilizing advanced imaging techniques and biomarkers can lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses.
Optimal Treatment Strategies: Ensuring access to specialized surgical expertise and comprehensive chemotherapy regimens is crucial for improving patient outcomes.
Promoting Research: Further research is needed to understand the specific genetic and environmental factors contributing to ovarian cancer in the Indian population to develop targeted prevention and treatment strategies.
By addressing these challenges through collaborative efforts involving healthcare professionals, policymakers, and the community, it is possible to reduce the risks and improve the outcomes for Indian women facing ovarian cancer.
Tags: