Powering Progress

October 15, 2025
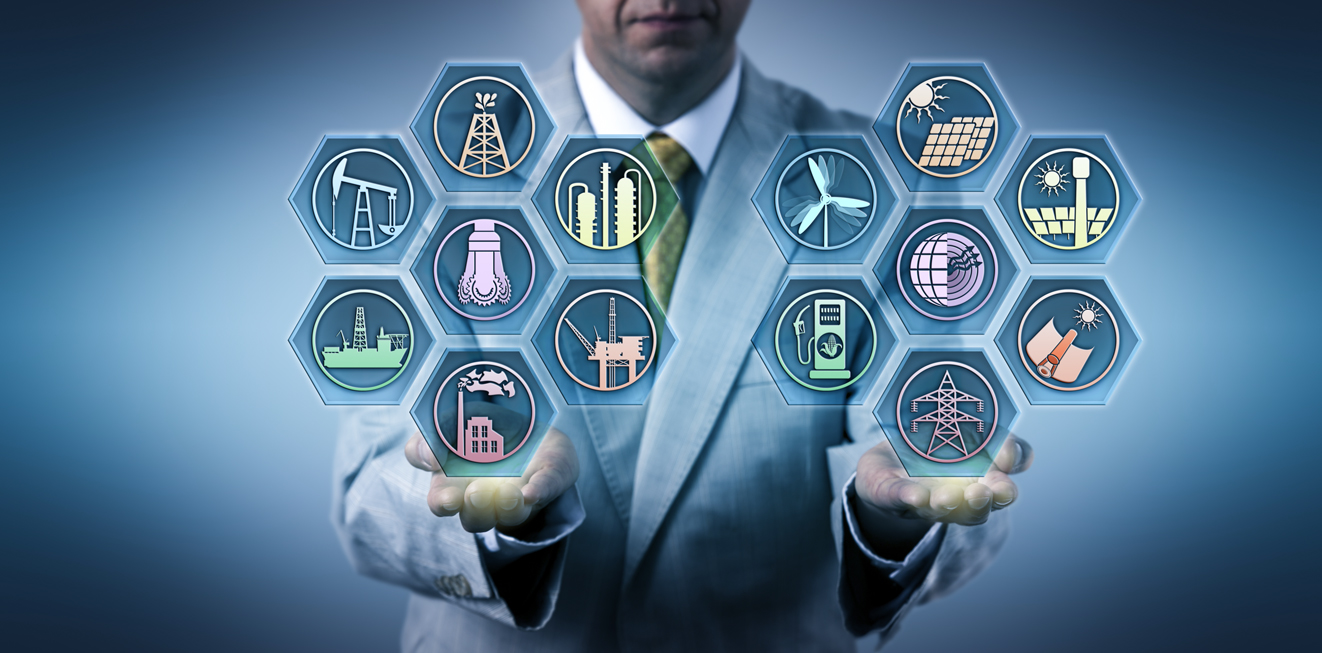
The Indian utilities sector—encompassing power (electricity, gas) and water—is at a critical inflection point. Driven by rapid urbanization, ambitious renewable energy targets, and the persistent challenge of system losses and aging infrastructure, the need for intelligent management has never been greater. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its complementary technologies like Machine Learning (ML), IoT (Internet of Things), and Generative AI (GenAI), are emerging as the fundamental tools to drive this transformation, promising a future of efficiency, resilience, and better service delivery.
The AI Revolution Across the Utilities Value Chain
AI is not just an incremental upgrade; it is enabling a holistic shift from reactive management to proactive, predictive, and eventually, autonomous operations across the Indian utility landscape.
1. Smart Grid Optimization and Stability (Power)
With India's ambitious push towards 500 GW of non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030, integrating intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind into the existing grid is a major challenge. AI provides the real-time intelligence needed for this integration:
Renewable Energy Forecasting: ML models analyze historical data, weather patterns, and real-time sensor data to accurately predict solar and wind power generation. This reduces supply variability, helping grid operators ensure stable power supply and prevent blackouts.
Load Balancing and Demand Forecasting: AI accurately predicts consumer electricity demand at a granular level (sector-wise, hyperlocal). This allows utilities to manage power dispatch efficiently, reducing operational costs and ensuring the grid can handle sudden surges, particularly with the rise of Electric Vehicles (EVs).
Non-Technical Loss (NTL) Reduction: AI-driven anomaly detection analyzes smart meter and distribution data to flag irregular usage patterns, effectively identifying and preventing energy theft (fraud), a significant issue in the Indian power sector.
2. Water Resource Management and Efficiency (Water)
For the water sector, where resource scarcity and distribution losses are severe, AI's role in conservation and public safety is paramount:
Leak Detection and Network Optimization: AI algorithms analyze data from IoT sensors and GIS (Geographic Information System) information within water pipelines. By identifying subtle changes in pressure or flow, they can pinpoint the exact location of leaks or pipe anomalies faster than traditional methods, drastically reducing Non-Revenue Water (NRW).
Water Quality Monitoring: AI-enabled sensors continuously monitor water for contaminants in real-time. ML models process this data to provide early warnings for contamination events, ensuring public health and enabling rapid response.
Reservoir Operation and Flood Management: Integrating satellite and meteorological data, AI can be used for better inflow forecasting, optimizing reservoir releases for hydropower generation while also aiding in flood and drought simulations for disaster preparedness, a critical need driven by climate variability.
3. Predictive Maintenance and Asset Longevity
For aging infrastructure—from transformers and turbines to pipes and transmission lines—AI shifts maintenance from a fixed schedule to a condition-based model:
Failure Prediction: ML models process vibration, temperature, and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) data from critical equipment. They learn the "normal" operational profile and predict the likelihood of failure, allowing maintenance teams to intervene before an outage occurs.
Drone and Image Analytics: Drones capture images of extensive utility networks, which AI then analyzes to automatically identify damaged components (e.g., chipped insulators, rusted towers) or vegetation encroachment, dramatically cutting inspection costs and time.
4. Enhancing Customer Experience
AI-powered solutions are improving interaction and transparency for the Indian consumer:
Intelligent Automation: GenAI and cognitive AI tools automate customer service, handling complex queries like "high bill" inquiries by analyzing historical usage and generating personalized, easy-to-understand explanations.
Personalized Engagement: Utilities can use AI to proactively advise customers on peak-hour usage, offering dynamic pricing models, and providing real-time outage updates via mobile or email, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
Indian Momentum and Case Studies
AI adoption is steadily gaining ground among progressive Indian utilities:
Tata Power-DDL & NTPC: These players are known for exploring AI-driven solutions for predictive maintenance, smart grid management, and tackling commercial losses.
ReNew Power: This Indian renewable energy company has leveraged AI to optimize the energy output of its solar and wind installations, leading to efficiency improvements and minimizing service interruptions.
Chennai Metropolitan Water Supply and Sewerage Board: The department has shared insights on its smart water management and urban governance initiatives, highlighting the integration of technology for efficient water supply.
Challenges on the Path to AI Adoption
Despite the immense potential, the Indian utilities sector faces hurdles in full-scale AI implementation:
1. Data Infrastructure and Quality: Many legacy systems struggle to provide the high volume, velocity, and quality of data required to train robust AI/ML models. A fragmented data landscape across different departments remains a significant challenge.
2. Lack of Technical Skills: A shortage of professionals with expertise in data science, AI engineering, and domain knowledge (utility operations) makes internal development and maintenance of sophisticated AI solutions difficult.
3. Capital Expenditure: The initial investment required for new sensors, smart meters, robust cloud infrastructure, and AI platforms can be substantial, particularly for smaller, state-owned utilities.
4. Cybersecurity Risk: As operations become increasingly digitized and interconnected, the threat landscape expands. AI systems themselves, while offering protection, must be rigorously secured against sophisticated cyberattacks.
An Intelligent Future
The role of AI in managing India's utilities is evolving from a technological novelty to an operational imperative. By solving core challenges like energy theft, distribution losses, and grid instability, AI is essential not just for efficiency, but for achieving national goals related to renewable energy integration and reliable public services. For India to realize the vision of "Viksit Bharat @2047" (Developed India), a strong, resilient, and intelligent utilities backbone, powered by AI, is non-negotiable. The collaborative effort between government bodies, research institutions, and utility providers will be key to turning AI's vast potential into tangible, nationwide progress.
—-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Want more branding articles to be utilised for growing upwards? Connect with us on
contact@upshotbrandmedia.com or on call at +91 8962429492
Tags: